- +1 (909)-728-2512
- info@onlinefirstaidcpr.com
- Greater Los Angles, CA
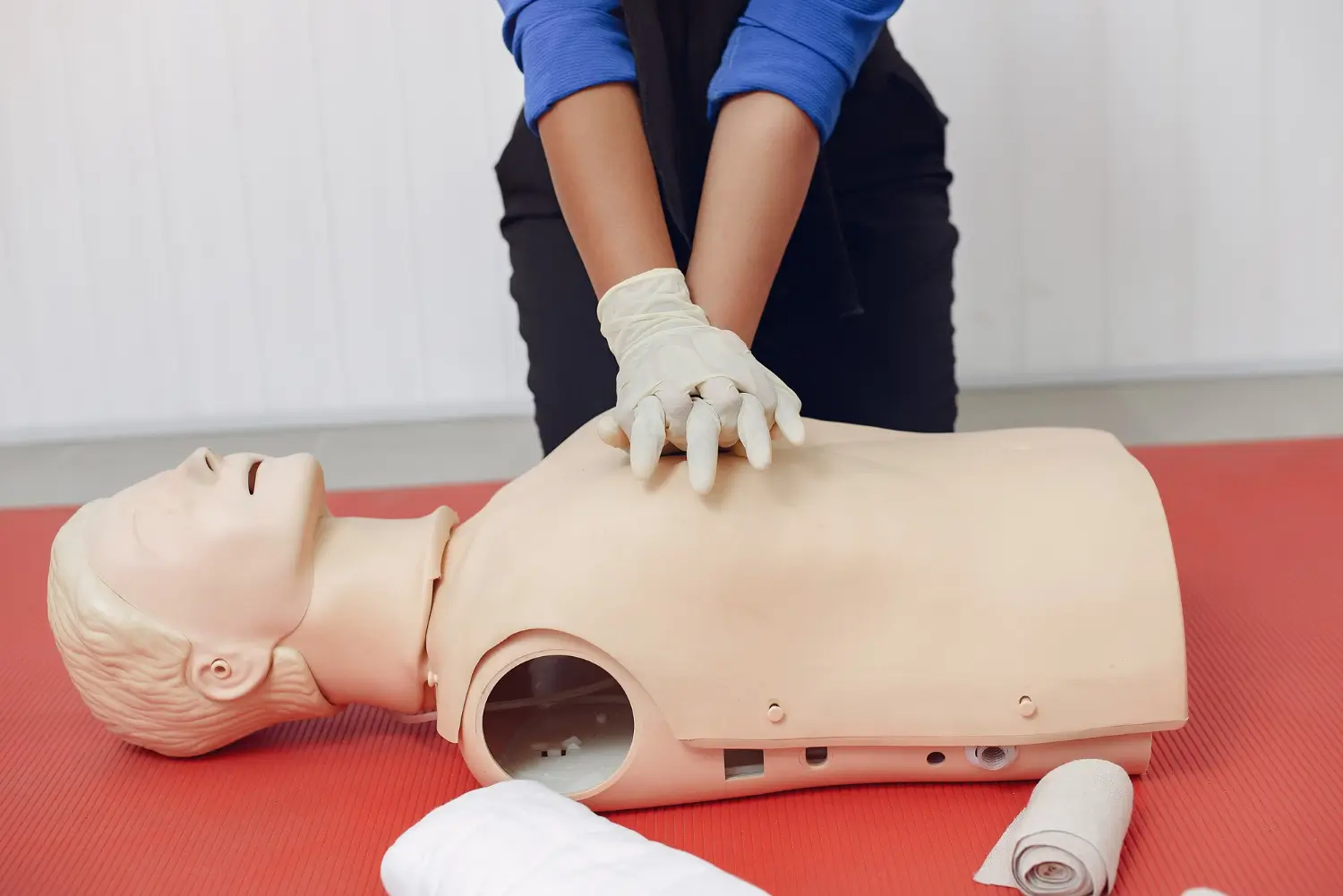
CPR For Adults and Children
Adult CPR
Adult Age: Puberty signs and older
- Female: Breast development signs
- Male: acial or underarm hair
Rescue Breaths:
Keep the airway open.Apply a face mask or pinch the nose. Breathe-in a regular-sized breath.Provide 2 rescue breaths for 1 second each. Observe for chest rise. Continue compressions straight away.
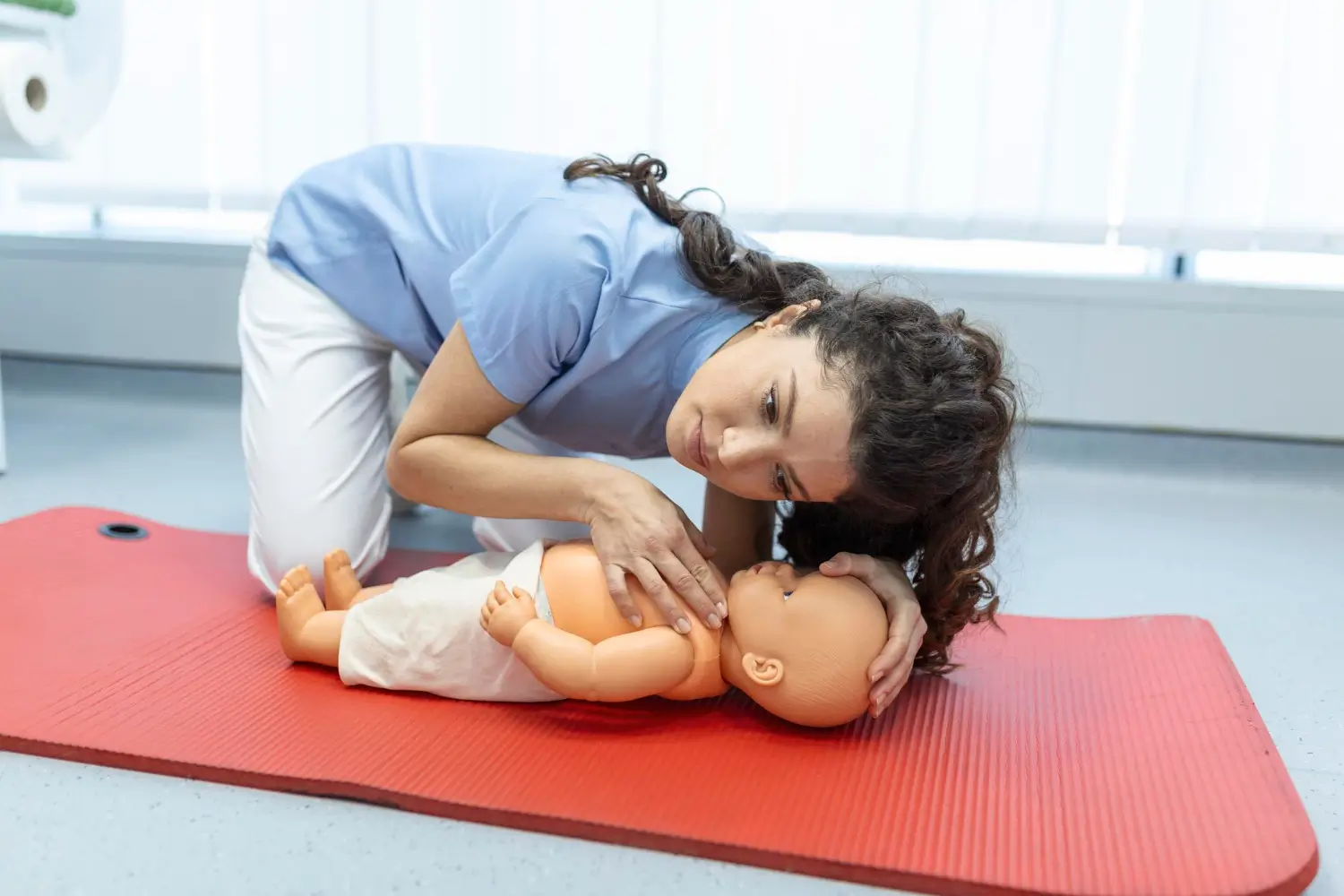
Child CPR
In children, the cardiac arrest usually occurs due to respiratory arrest and not due to a heart problem. Common causes include poisoning, injury, drowning, choking, and asthma.
Check Response & Call 911:
- Tap the child‘s shoulder and shout.
- If there is no response, call for help.
- Tell a bystander to call 911 and get the AED yourself.

Child or Adult Choking
A serious airway blocking is life-threatening. Identify a choking emergency and act fast. The technique to manage choking is the same for adults and children of age 1 and older. To tell the difference between choking and other emergencies, look for the universal sign of choking: one or both hands at the throat. Suspect choking when someone unexpectedly stops talking.
Mild Chocking
A person with a mild airway block can cough forcefully or speak. Do not interfere. If the person can speak, he can breathe also. Encourage coughing, and check if the airway blocks severely.
Severe Chocking
A person with a severe airway block cannot breathe, cough effectively, or speak. He may make a high-pitched sound when inhaling or turn blue around the lips and face.
Cold Related Emergencies
Help :
- Shift to a warm location.
- Call 911.
- Gently take off wet clothing, dry the skin, and wear dry clothing.
- Wrap the head and neck in blankets.
- Try to re-warm the person by moving him near a heat source, or with heating pads, or with containers of warm water, if emergency help is delayed. Maintain safe distance between the skin and the heat source.
- If the victim is alert, give warm liquids. Avoid alcohol or caffeine.
- Observe response and breathing.
